The Internet of Things (IoT) is anticipated to become essentially over the coming years. Research firm Gartner Inc. has assessed that 8.4 billion associated things were being used worldwide in 2017, up 31% from 2016, and anticipates that the number will achieve 20.4 billion by 2020.
Consider the sheer number of IoT gadgets that will be associated with the Internet and how much information will be produced by those gadgets. By 2025, the IoT is anticipated to have 75.44 billion associated gadgets. At that point, almost a fourth of the world’s anticipated 163 zettabytes of information will have been made progressively and 95% of that information will have been made by IoT gadgets.
To guarantee solid security for IoT and IIoT, associations would be insightful to execute a few accepted procedures, as prescribed by IEEE in a 2017 report.
Device Security :
Afterward, as the universe of malware extended and methods for maintaining a strategic distance from recognition progressed, whitelisting procedures began supplanting boycotting. Likewise, as more gadgets began going onto corporate systems, different access control frameworks were created to validate both the gadgets and the clients sitting behind them and to approve those clients and gadgets for particular activities.
All the more as of late, worries over the realness of programming and the assurance of licensed innovation offered to ascend to different programming confirmation and authentication procedures regularly alluded to as trusted or estimated boot. At long last, the privacy of information has dependably been and remains an essential concern. Controls, for example, virtual private systems (VPN) or physical media encryption, for example, 802.11i (WPA2) or 802.1AE (MACsec), have created to guarantee the security of information in movement. NEW THREATS, CONSTRAINTS, AND CHALLENGES Applying these same practices or variations of them in the IoT world.
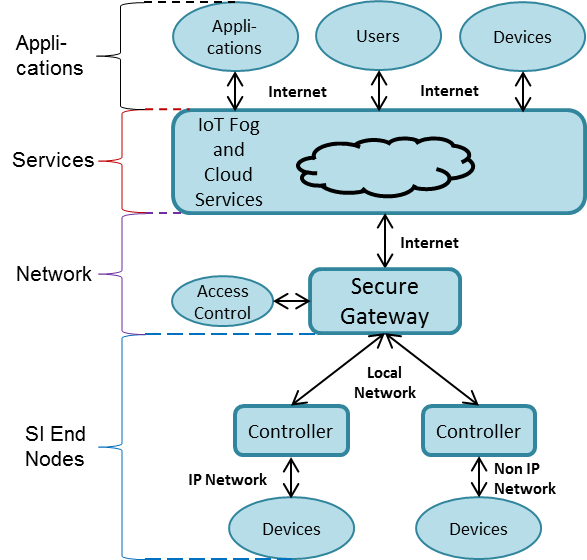
Network security:
Notwithstanding gadgets, organizations need to guarantee that the systems they use for IoT and IIoT are secure. This incorporates the utilization of solid client confirmation and access control components to ensure just approved clients can access systems and information. Passwords must be modern enough to oppose instructed speculating thus called savage power strategies, IEEE notes. Wherever conceivable associations should utilize two-factor validation (2FA), which expects clients to enter a secret word and in addition utilize another confirmation factor, for example, an arbitrary code created by means of SMS content informing. For IoT applications, it’s a smart thought to utilize setting mindful validation (or versatile verification). This includes the utilization of relevant data and machine-learning calculations to continually assess dangers without affecting the client’s understanding.
The utilization of solid encryption to anchor conventions is another great system security rehearses. Any correspondences between gadgets can possibly be hacked, and both IoT and IIoT include a large number of system conventions utilized at different layers. The utilization of both system layer and transport layer encryption can give various impediments to arrange based assaults.